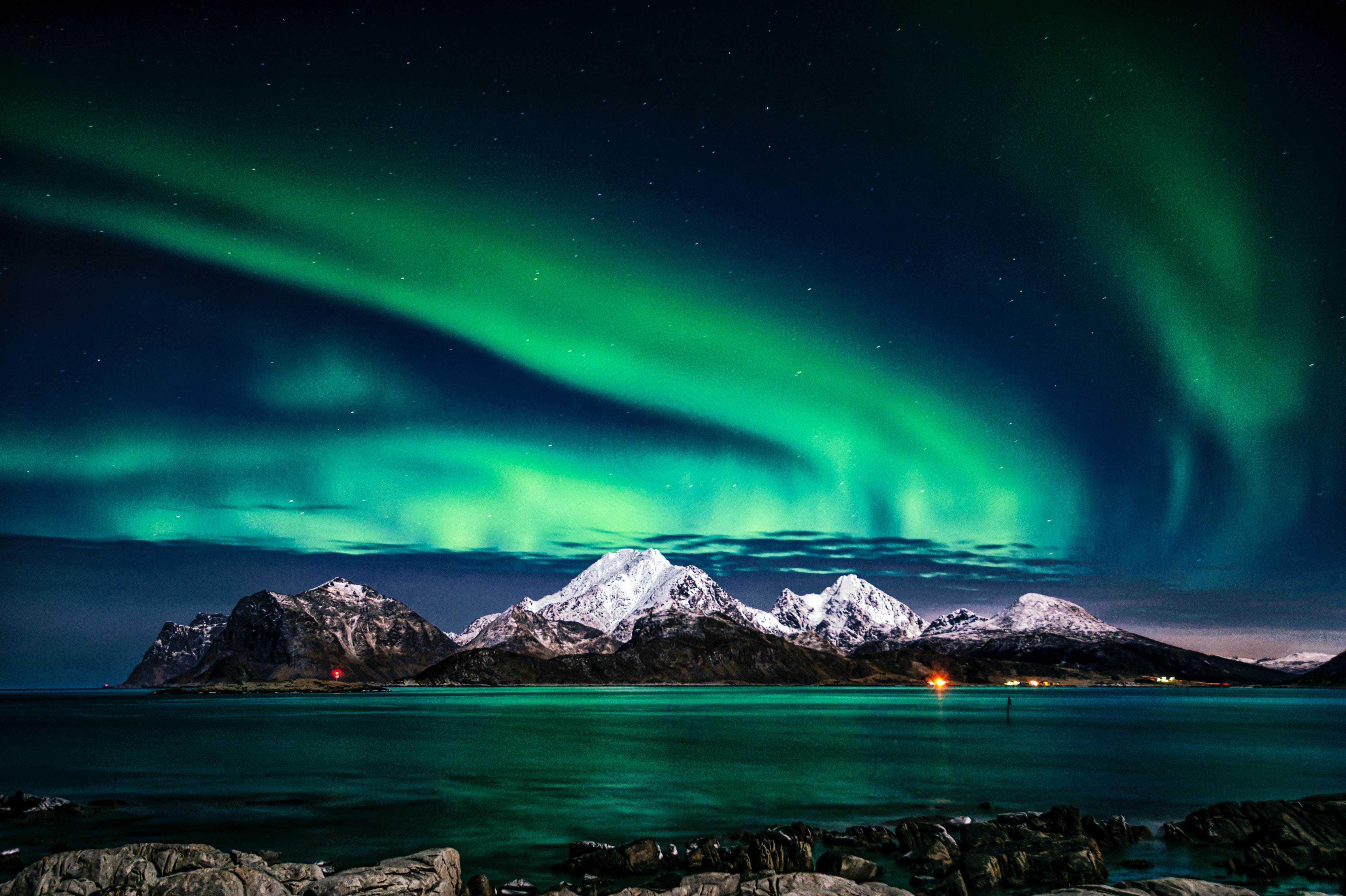
Have you ever seen the skies light up with dancing colors of green, pink, and purple? If not, then you must plan a trip to the Arctic and witness the stunning display of Aurora Borealis, also known as the Northern Lights. This natural light show is one of the most magnificent and magical phenomena that can be seen from the Northern Hemisphere. From ancient legends to modern science, Aurora Borealis has always been a subject of fascination and awe for people worldwide. In this blog, we will explore the science behind Aurora Borealis, its origin, and the best places to experience this mesmerizing natural light show.
The Science Behind Aurora Borealis:
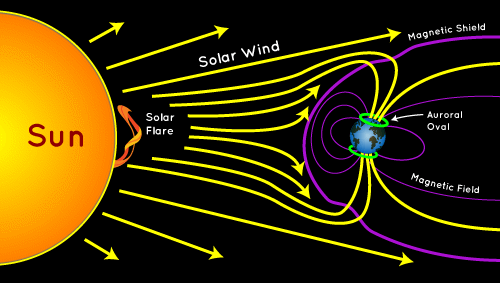
The science behind Aurora Borealis is a fascinating subject that combines various fields of study, including physics, chemistry, and astronomy. Aurora Borealis occurs when charged particles from the sun, also known as the solar wind, interact with the Earth's magnetic field and enter the atmosphere. The charged particles are mostly electrons and protons that are accelerated to high speeds by the sun's magnetic field and then travel through space towards Earth.
As these charged particles approach the Earth, they encounter the Earth's magnetic field, which acts as a shield and deflects most of the particles away from the planet. However, some particles manage to penetrate the magnetic field and enter the atmosphere near the magnetic poles, where the field is weakest. When these particles enter the atmosphere, they collide with atoms and molecules, mostly oxygen and nitrogen, that are present in the atmosphere.
During these collisions, the charged particles transfer their energy to the atoms and molecules, exciting them to higher energy levels. When the excited atoms and molecules return to their original state, they release the excess energy in the form of photons, which we see as light. The color of the light depends on the type of atom or molecule involved in the collision and the altitude at which the collision occurs.
For instance, when charged particles collide with oxygen molecules at an altitude of about 60-150 miles above the Earth's surface, the green light is produced. The green light is the most common color of Aurora Borealis, and it results from the excitation of atomic oxygen, which then emits a green photon as it returns to its ground state. Similarly, when charged particles collide with nitrogen molecules at the same altitude, they produce the pink color of Aurora Borealis.
The purple color of Aurora Borealis is much rarer and occurs at higher altitudes, around 60 miles or above. This color is produced by the excitation of molecular nitrogen, which emits a purple photon as it returns to its ground state.
The Colors of Aurora Borealis:
The most common colors of Aurora Borealis are green and pink, which are caused by the collision of charged particles with oxygen molecules at an altitude of 60-150 miles above the Earth's surface. The green color is produced when the particles collide with oxygen molecules, and the pink color is produced when the particles collide with nitrogen molecules. The purple color is rare and is caused by the collision of charged particles with nitrogen molecules at an altitude above 60 miles.
The Origin of Aurora Borealis:
The ancient cultures of the Arctic believed that Aurora Borealis was the dancing spirits of their ancestors. In Norse mythology, Aurora Borealis was the light from the shields of Valkyries, the female warriors who chose the bravest soldiers to join Odin in Valhalla. However, it was not until the 19th century that the scientific explanation of Aurora Borealis was discovered.
Best Places to Witness Aurora Borealis:
The best time to witness Aurora Borealis is during the winter months from September to March, and the best places to experience this natural light show are in the Arctic regions. Norway, Finland, Sweden, Iceland, and Canada are some of the best places to witness Aurora Borealis. The Northern Lights can also be seen from Alaska, Russia, and Greenland. To increase your chances of witnessing Aurora Borealis, you should plan your trip to coincide with the new moon phase, which will provide a darker sky for a clearer view of the Northern Lights.
Conclusion:
Aurora Borealis is a natural light show that is not only beautiful but also a scientific wonder. Witnessing Aurora Borealis in the Arctic sky is an experience that one will never forget. From the ancient legends to the modern science, Aurora Borealis has always been a subject of fascination and awe for people worldwide. So, if you haven't witnessed this mesmerizing natural light show yet, pack your bags and head to the Arctic to experience the enchanting display of Aurora Borealis.
Discover More
Most Viewed
Christmas is a season of joy, love, and traditions. And what better way to get into the holiday spirit than through timeless carols? These musical gems have been bringing people together for generations. Here’s our ranked list of the Top 10 Christmas Caro…
Read More