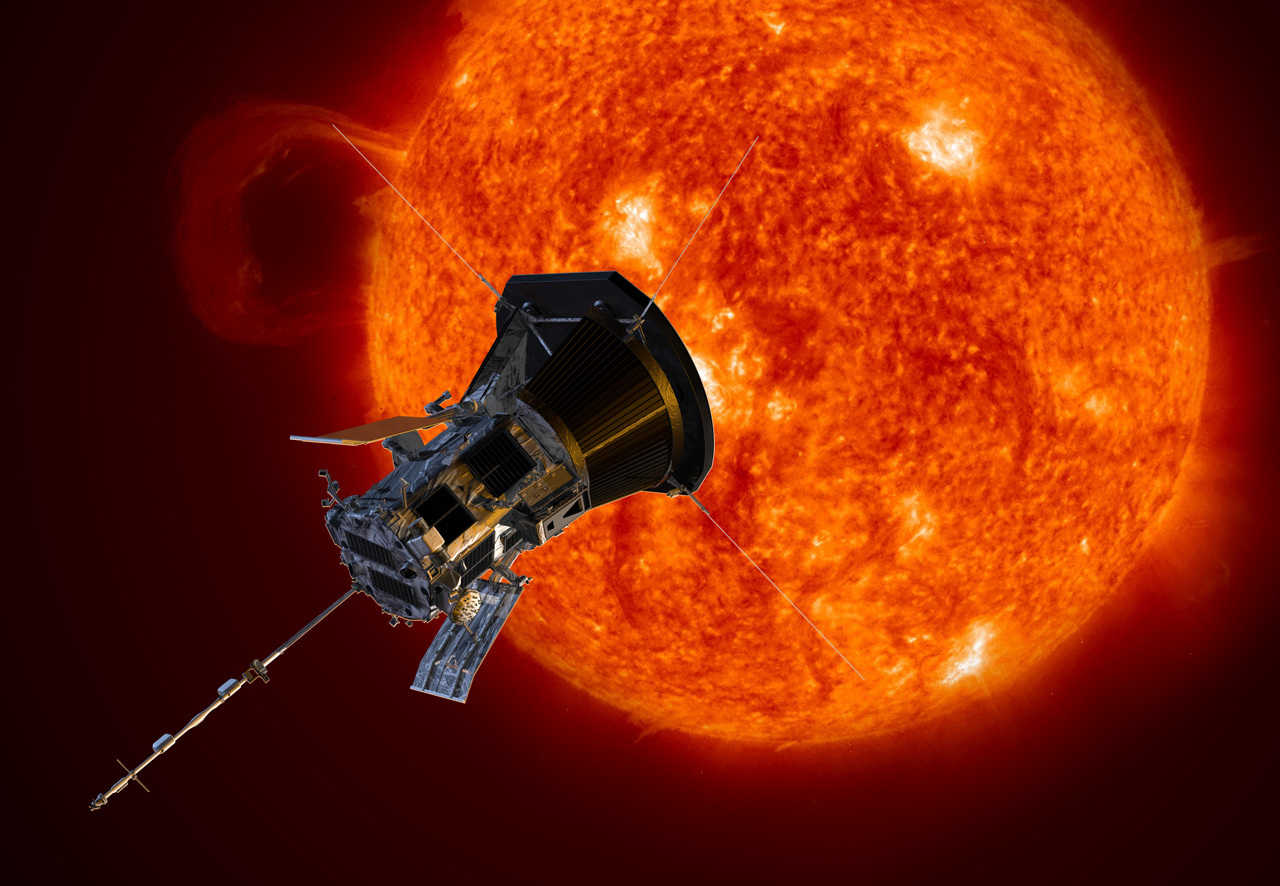
What is the Parker Solar Probe?
The Parker Solar Probe, launched by NASA, embarks on a historic quest to "touch the Sun." It represents a significant leap in proximity to the Sun compared to any previous spacecraft, promising to transform our comprehension of our nearest star.
This ambitious mission entails the Parker Solar Probe flying within the Sun's vicinity over seven times closer than any other spacecraft to date. Throughout a span of seven years, the probe is scheduled to complete 24 orbits around the Sun, with its closest approach bringing it within approximately 3.9 million miles (6.2 million kilometers) of the Sun.
| Nation | United States of America (USA) |
| Objective(s) | Solar Orbit |
| Spacecraft | Parker Solar Probe (Solar Probe Plus) |
| Spacecraft Mass | 1,510 pounds (685 kilograms) at launch |
| Mission Design and Management | NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center / Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory |
| Launch Vehicle | Delta IV-Heavy with Upper Stage |
| Launch Date and Time | Aug. 12, 2018 / 7:31 UTC) |
| Launch Site | Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. |
| Scientific Instruments | 1. Fields Experiment (FIELDS) 2. Integrated Science Investigation of the Sun (ISOIS) 3. Wide Field Imager for Solar Probe (WISPR) 4. Solar Wind Electrons Alphas and Protons (SWEAP) |
Source: NASA Visualization Technology Applications and Development (VTAD)
The Latest News About the Parker Solar Probe:
NASA's Parker Solar Probe has achieved a significant milestone by venturing into the realm of fast solar winds and unveiling their source. These high-speed streams of charged particles emanate from the Sun, reaching speeds of up to 1 million miles per hour. As the closest spacecraft ever to the Sun, the Parker Solar Probe's groundbreaking data will enhance our understanding of solar behavior and its impact on Earth.
On February 25, 2023, the Parker Solar Probe courageously traversed the fast solar winds, traveling at a remarkable velocity of 430,000 miles per hour while passing within a mere 4.3 million miles of the Sun's surface. This remarkable proximity has never been achieved before.
Analysis of the Parker Solar Probe's data has elucidated the origin of fast solar winds, which can be attributed to the Sun's twisted and tangled magnetic fields generated on its surface. These magnetic fields exert a force that expels charged particles away from the Sun.
The insights gained from the Parker Solar Probe's data hold immense value in unraveling the mysteries of solar activity and its impact on Earth. By predicting solar storms, which can disrupt satellites and power grids, scientists can take proactive measures to safeguard our planet.
The Parker Solar Probe mission is an ongoing endeavor, with the spacecraft continuing its orbit around the Sun and collecting vital data. This wealth of information will empower scientists to deepen their understanding of the Sun and its influence on our planet.
Summary:
- NASA's Parker Solar Probe is a mission aimed at "touching the Sun" and revolutionizing our understanding of it.
- The spacecraft will fly closer to the Sun's surface than any other spacecraft before.
- Over a span of seven years, it will complete 24 orbits around the Sun.
- At its closest approach, the spacecraft will come within about 3.9 million miles (6.2 million kilometers) of the Sun.
- The mission is managed by NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center and Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory.
- The launch vehicle for the Parker Solar Probe was the Delta IV-Heavy with Upper Stage.
- The spacecraft was launched on August 12, 2018, from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
- It carries several scientific instruments, including the Fields Experiment (FIELDS), Integrated Science Investigation of the Sun (IS☉IS), Wide Field Imager for Solar Probe (WISPR), and Solar Wind Electrons Alphas and Protons (SWEAP).
Implications for humanity:
The Parker Solar Probe's remarkable discovery of the origin of fast solar winds signifies a major breakthrough in solar research. It offers profound insights into the functioning of the Sun and its repercussions for our planet. Armed with this knowledge, scientists can develop strategies to shield satellites and power grids from the damaging effects of solar storms.
The Parker Solar Probe is an exceptional mission that unveils the Sun's secrets, enabling us to comprehend its profound influence on Earth. The data gathered by the spacecraft will continue to serve as an invaluable resource for scientists for years to come.
Discover More
Most Viewed
Christmas is a season of joy, love, and traditions. And what better way to get into the holiday spirit than through timeless carols? These musical gems have been bringing people together for generations. Here’s our ranked list of the Top 10 Christmas Caro…
Read More